About Me

I completed my undergraduate studies in the Department of Computer Science and Technology at Tongji University and am currently working as a research assistant at the MAPLE Lab at Westlake University. My research interests include multimodal large models, safety supervision mechanisms and simulations for autonomous driving, as well as virtual reality. Currently, I am primarily focused on exploring the applications of large models in fine-grained emotional computation and multimodal recommendation systems.
During my undergraduate studies, I led a team to establish two startups aimed at developing mental health applications based on extended reality technologies and large language models. Our team has successfully developed two applications, which are actively being improved and tested. The project has received support from two startup funds and has won over ten awards in various innovation and entrepreneurship competitions both domestically and internationally.
If you are interested in my research directions or startup projects, or are looking for any form of collaboration, please feel free to email me at 2054310@tongji.edu.cn.
Educations
.png)
Tongji University
Bachalor Degree(2020 - 2024)
.png)

SRIAS / Tongji
Research Assistant(2022 - 2023)
Westlake University
Research Assistant(2024 - )
Publicatons
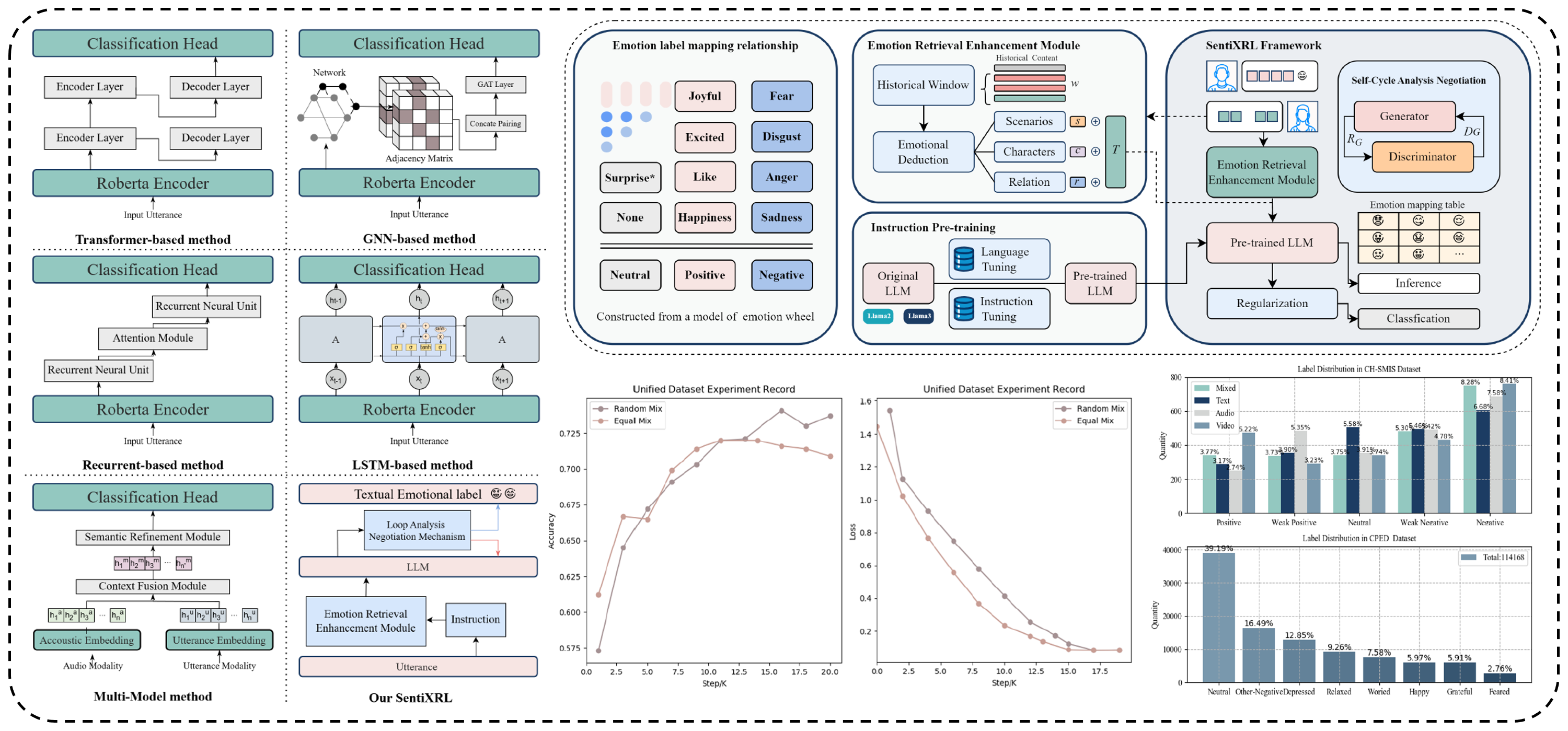
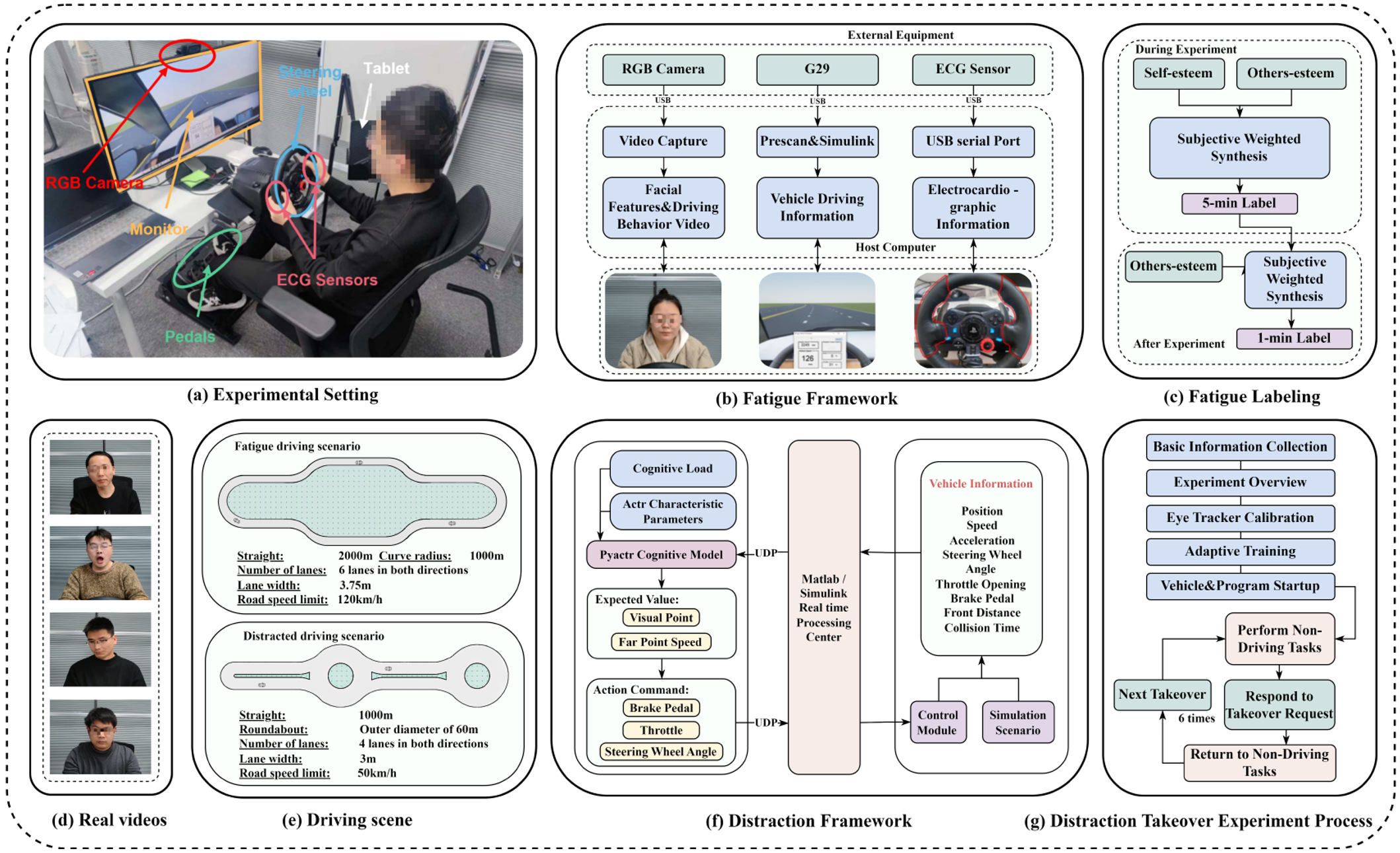
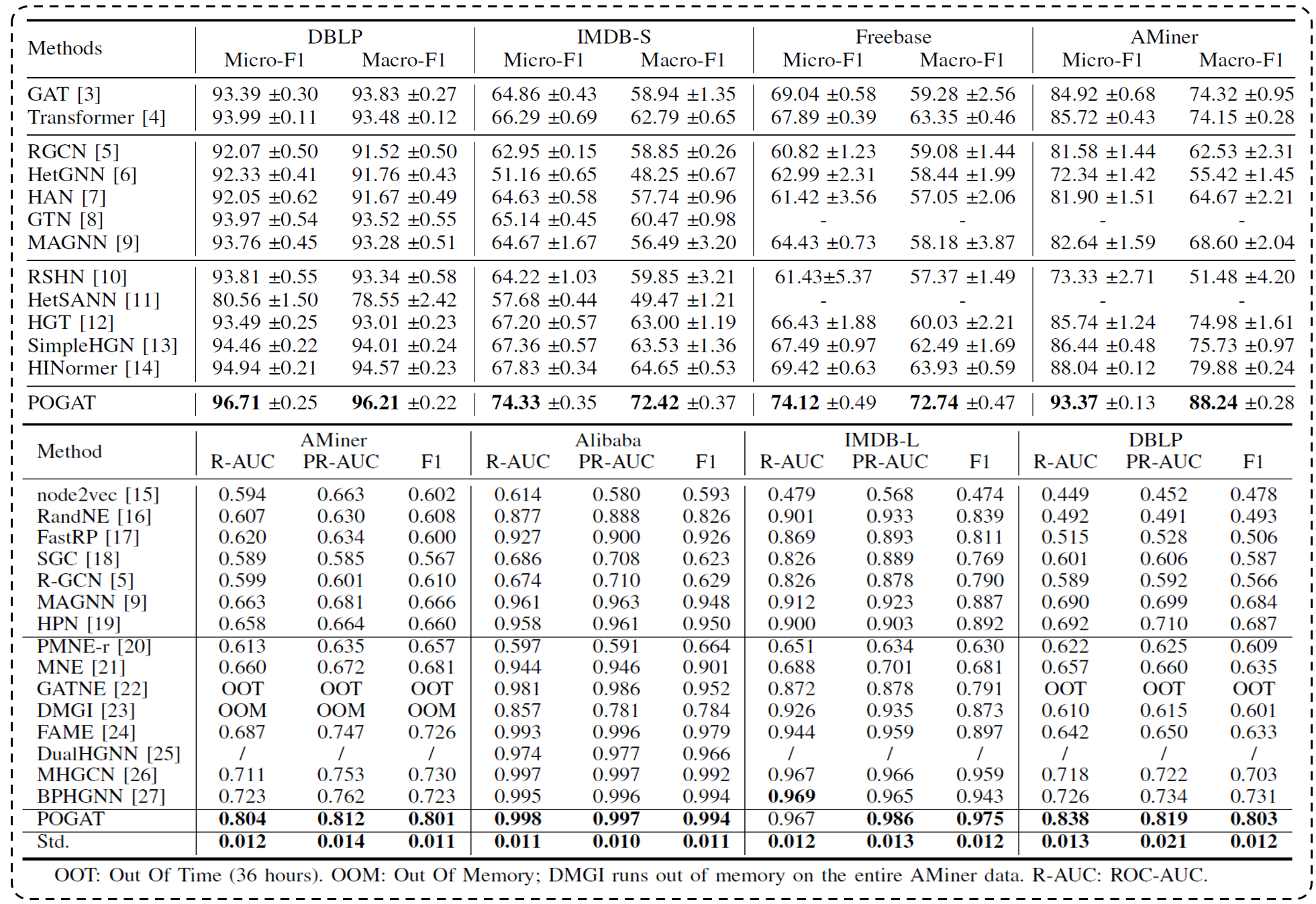

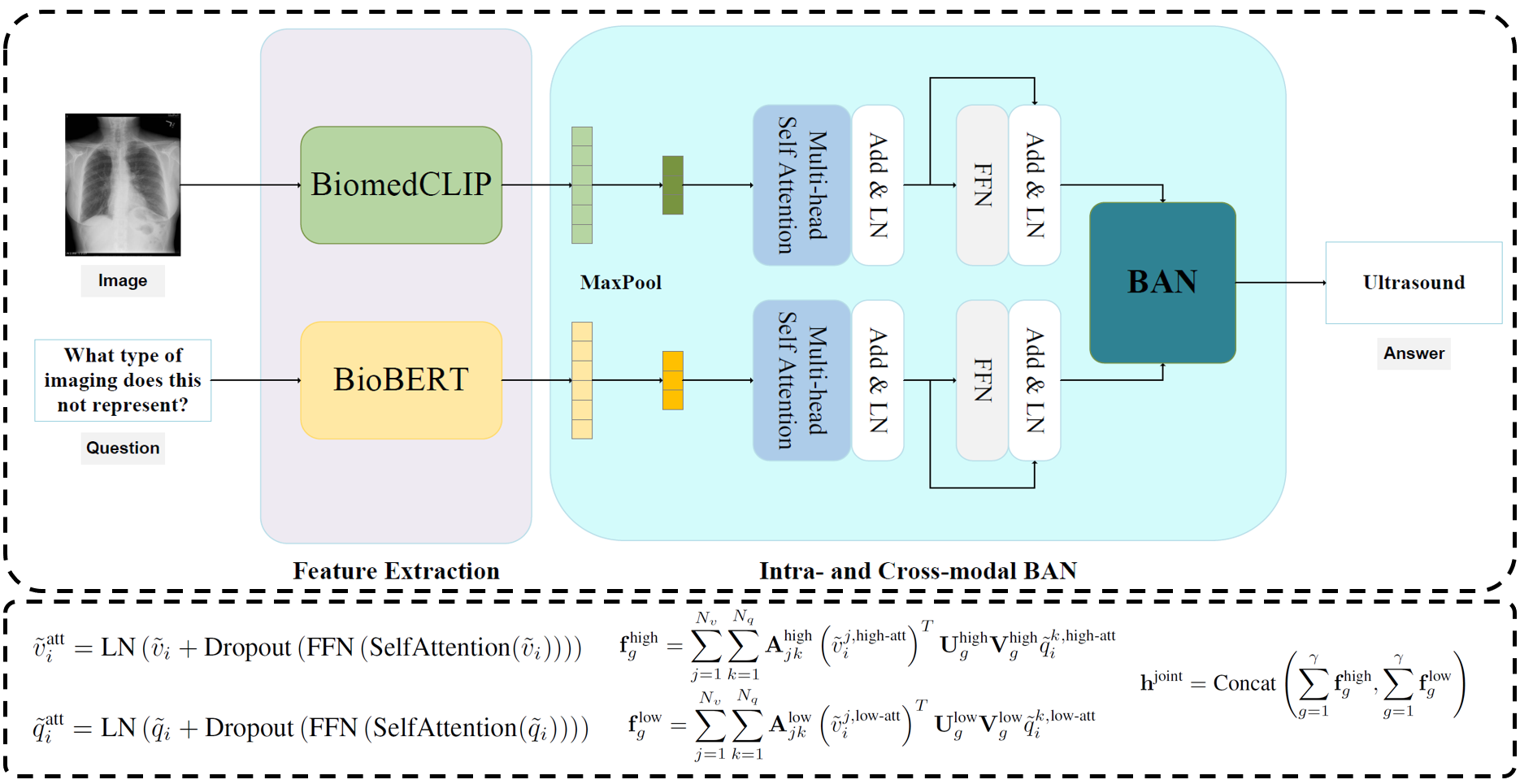
Intellectual Property
Honors and Awards
Internship & Summer School


Entrepreneurship

● Developed a well-rounded, multi-platform application using VR/AR technology and deep learning to combine traditional psychological healing techniques and reduce the reliance on psychological consultants.
● Established and led a startup team, expanding the team to nearly 50 people.
Project Introduction

Considering the increasingly deteriorating mental health of the younger population and the growing risks of psychological issues, coupled with the shortage of mental health professionals and the general public's lack of awareness of mental health, there is a noticeable gap in applications addressing mental healing and stress relief. While AR technology has advanced significantly, particularly in mobile applications, it is predominantly used in B2B settings, mainly for product promotion, with limited progress in other fields. Taking into account the current market landscape and technological considerations, we have developed a multi-platform XR interactive application focused on mental healing and stress relief, providing an innovative solution for psychological well-being.









